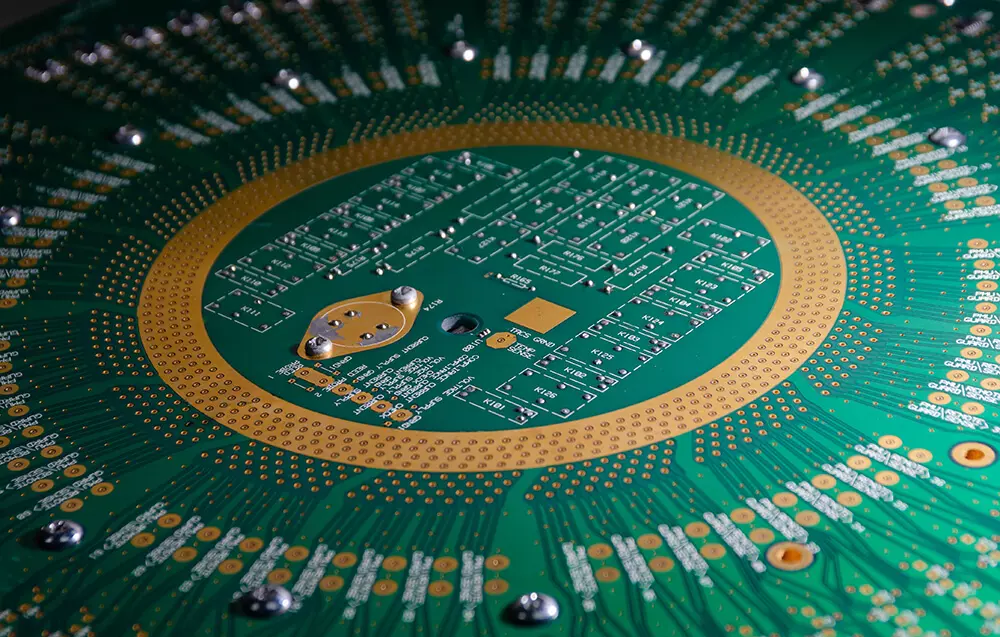
Various Types of PCB (Printed Circuit Boards)
1. Single sided PCBs
Single sided printed circuit boards are circuit boards with one layer of conducting material on one side of the board, while the other side is used for incorporating different electronic components. A single sided board is made of a substrate layer, a conductive metal layer and followed by a protective solder mask and silk screen. Single sided circuit boards were the first printed circuit board technology and have been in circulation since the 1950s, and remain one of the most commonly used circuit boards due to their simple design.
Benefits of single sided PCBs
Single sided circuit boards are relatively simple when it comes to their design meaning they require fewer resources and subsequently have a low density. This combination allows for highly cost-effective and affordable manufacturing, as due to their simplicity they can be produced at higher speeds in larger quantities with less potential problems to encounter and without losing the high-quality performance ABL strive to produce. Additionally, this means a shorter lead time for clients as these boards can be produced at speed and in bulk with ease, compared to multi-layer PCBs.
Single sided PCB applications
As these circuit boards are straightforward to produce and ideal for simple, low-density designs, this means they are one of the most commonly produced boards. Whilst their design and manufacturing may be simple they can still be used in many complex electronic devices, such as radio and stereo equipment, printers and even vending machines.
Because they can be produced in high quantities, with relatively low production costs, single sided PCBs are the board of choice for many. However, it is important to consider the needs of your project and whether a single sided PCB provides the capabilities and functionalities needed.

2. Double sided PCBs
Double sided PCBs are a popular choice in the industry when it comes to printed circuit boards, as they allow for more complex designs, circuits and thus benefits for products.
Unlike single sided PCBs, double sided PCBs can mount the conductive copper and components on both sides of the board, as opposed to just the one. These double sided boards allow for closer routing traces as they can alternate between the top and bottom layers using vias. This can be very useful in many electronic products as the circuits on one side of the board can be connected to the other with the help of holes drilled onto the board.
Benefits of double-sided PCBs
Due to how they’re manufactured, double sided PCBs are a great choice thanks to their ease of use and flexibility. They also offer increased circuit density as the second layer means there is more capacity for PCB components than on single sided PCBs.
With this increased space, double sided PCBs use a more complex circuitry, meaning they are great for more advanced electronic systems such as lighting and car dashboards. These benefits can also come with a reduction in production cost because double sided boards are often smaller in size than other PCBs.
3. Multilayer PCB
Many printed circuit boards have one or two conductive layers, being built on either a double-sided or a single-sided substrate. A multi-layer PCB is designed and manufactured using several layers of base materials. . Generally speaking, any board featuring at least three conductive layers is included in this category.
Multilayer PCBs are constructed using a ‘sandwich’ model, featuring numerous double-sided conductive layers separated by a corresponding number of insulating material sheets. These must all be bonded and laminated together under high pressures and temperatures, such that no air gaps remain and the final PCB assembly is sufficiently robust.
Are multilayer PCBs better than double-sided?
The answer here depends on the finished board’s intended application. While multi-layer designs are more expensive to produce, there are numerous scenarios in which they’re beneficial or essential. This is often because they allow for more complex circuits in a smaller footprint. Key advantages of multi-layer PCBs may include:
Improved durability – more layers stacked together makes for a more robust physical design
Overall quality – they’re inherently more complex to design and assemble, meaning the production process is often more meticulous
Better for more complex or high-power circuit designs – speed and capacity requirements for some performance devices may demand a multilayered PCB design
Space-saving – stacking conductive layers allows for reduced footprint, with larger circuits fitting on a smaller and more lightweight board
Single connection point – multiple separate PCBs would each need to be powered individually; a muti-layer design usually has just one such input
4. Rigid PCB
A rigid circuit board is the most traditional form of board in the PCB world. They remain hugely popular today and are used in many products consumers use daily. Rigid PCBs are a form of circuit board which are solid and inflexible in their structure and therefore cannot be bent or flexed. They’re made up of several different layers, such as a substrate layer, a copper layer, a solder mask layer and a silk screen layer, which are joined together via adhesive and heat. Whilst some circuit boards are only single sided, double sided or multilayered, rigid PCBs can take any of these forms depending on the requirements needed. However, once they have been manufactured they cannot be modified or changed.
Rigid PCB & benefits
Option that is cost-effective and can be produced in large quantities, then rigid PCBs are a good option for you. They also tend to be more durable than other boards like flexible PCBs, for example, so if you are looking for a hard-wearing circuit board a rigid PCB – with its increased circuit density – is a perfect choice.
Rigid boards are particularly popular in products and industries where it is vital that components remain fixed, as they can cope with both heat and high levels of stress during their lifespan.

Where are rigid PCBs used?
Rigid PCBs are used in many day-to-day products that we rely on for work and communication, such as:
GPS equipment
Computers, laptops, tablets and mobile phones
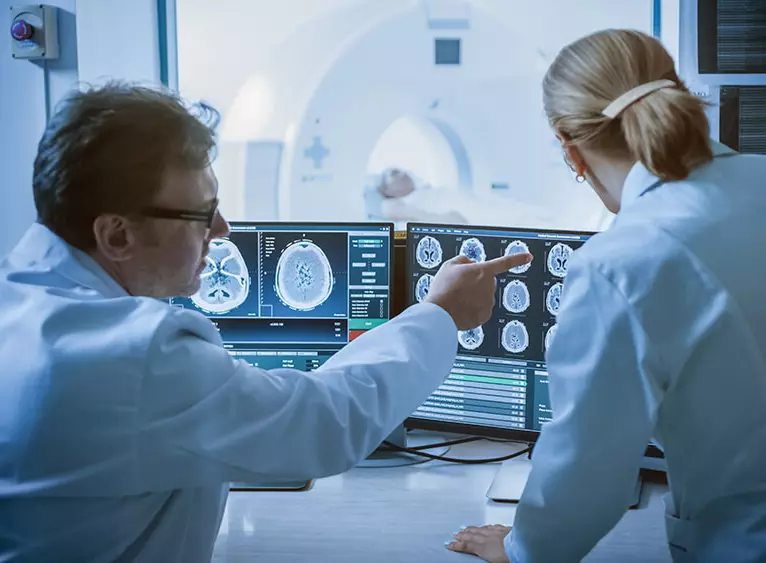
Additionally, they’re used in important medical equipment where they are mainly used in large, non-portable apparatus such as:
X-rays
Heart monitors
CAT scans
MRI systems
PCBs can withstand high temperatures thanks to their copper and aluminium substrates, which means they are also the perfect boards for the aerospace industry, where they’re used in a variety of essential equipment:
Airplane cockpit instrumentation
Temperature sensors
Control tower instrumentation
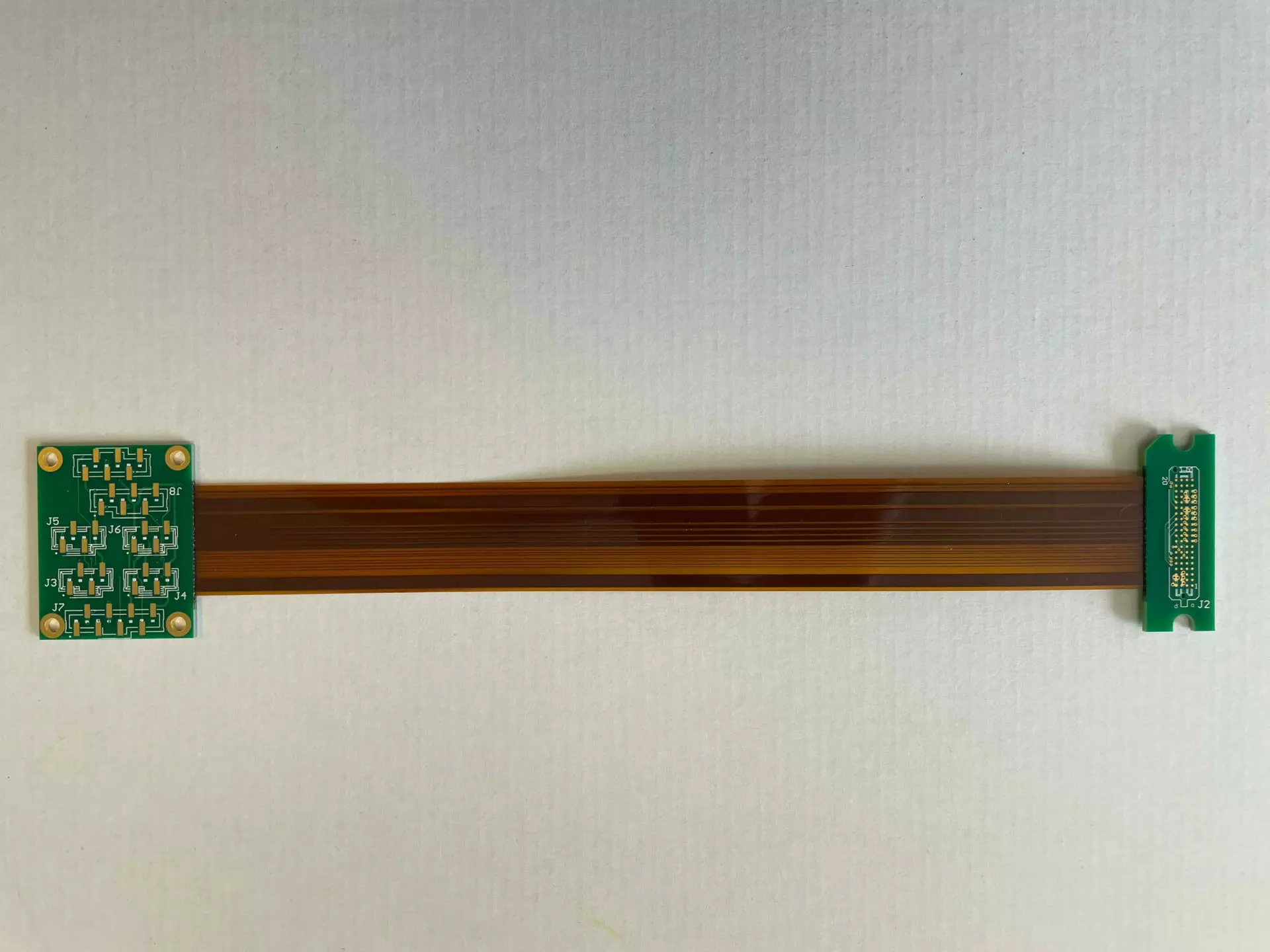
5. Flexible PCB
Flexible PCBs, also known as ‘flex PCBs’ or ‘flex circuits’, the main differentiating point is that the electronic devices are mounted onto flexible plastic substrates.
Instead of building a device in which the components must comply to the size of the circuit board, flex PCBs are instead designed to fit the device or product. Flex PCBs are usually thin, lightweight and can work exceptionally well in small spaces and in contoured shapes, which can be a challenge for other printed circuit boards.

Benefits of flexible PCB’s
There are several advantages of a flex PCB that are worth considering when thinking of the best foot forward for your all-important product:
Space Race: The nature and design of flex PCBs mean they do not use as much space, and additionally weigh less than an ordinary circuit board
Bend and Snap: As the name would suggest, flex PCBs also have inherent flexibility allowing for tighter bend capabilities for your product
Feeling The Heat: Flex PCBs, due to their substrates such as polyimide, dissipate heat better than most circuit board materials and are able to withstand extreme temperatures
Compatibility Test: Flexible printed circuit boards are compatible with a wide range of components or connectors, many being smaller or less expensive connectors
On top of the above benefits, flex PCBs also use less material, less packaging and the costs for replacements are lower, which can never be a bad thing! Flex PCBs offer a plethora of possibilities for different products and designs combining the best qualities of connectors, printed circuit boards, wires and cable, all in one interconnect.
6. Rigid-Flex PCB
A Rigid-Flex PCB is a hybrid circuit board combining elements of both flexible circuit boards and rigid circuit boards, with an end result of a board that is able to be folded or continuously flexed and is normally formed into a flexed shape or curve during the manufacturing process.
The flexible layers of a Rigid-Flex PCB are buried within the board and penetrate through the rigid sections of the PCB.
Rigid-Flex benefits
There are several benefits to a Rigid-Flex PCB which could make it a perfect choice for your product, including:
Reduced space requirement through 3D ability
Shock resistance: Rigid-Flex PCBs can withstand high-stress environments
Increased reliability: due to the reduced need for solder joints or connectors, Rigid-Flex PCBs are a brilliant choice for products where a connector or cable failure could be detrimental
Rigid-Flex PCBs also have a simpler assembly process as they have fewer cables and connectors being used throughout
If your product requires a board that needs to be folded when assembled or you’re after something highly durable and long-lasting then a Rigid-Flex PCB might be the right fit for you.
Flex to install & dynamic flex PCBs
There are two common types of Rigid-Flex PCBs; flex to install and dynamic flex.
Flex to install: this is the most common of the two and applies when a board only folds once, either when the device or product is assembled or dismantled, but is otherwise sturdy and stable throughout
Dynamic flex: a dynamic flex board will be used when a product is required to fold and bend when in use, meaning they are highly durable and can last through a thousand flex cycles
Whilst the design might be a touch more complex, and the process slightly more time consuming than the usual printed circuit board
7. HDI PCBs
HDI PCBs, known as High Density Interconnect PCBs, are one of the fastest-growing technologies available in the circuit board world. HDIs have higher circuitry density compared to more traditional circuit boards, such as single sided or double sided PCBs, and their design allows them to have smaller vias, smaller capture pads alongside higher connection pad densities.

HDI PCB benefits
his HDI technology allows designers and manufacturers to place more components on both sides of the PCB, if needed for your products. HDI boards also contain blind and buried vias, alongside micro vias which have a smaller diameter meaning designers are also able to place smaller components closer together on the board, resulting in quicker transmission of signals across and less signal loss or crossing delays.
The finer structures of a HDI PCB means they are extremely compact in size and have fewer layers compared to multi-layer PCBs, allowing for greater packaging density. Whilst they may be smaller in size, the HDI micorvia technology used to produce these boards means an 8 layer through-hold PCB can be reduced to a 4 layer HDI PCB whilst still having the same, or improved functions of a standard 8 layer PCB. Subsequently, what an HDI PCB lacks for in size, it makes up for in quality.
Applications of HDI PCBs
HDI PCBs are used in advanced technology systems such as smartphones and games consoles. They are also making a huge impact on the medical industries as their small size means they can fit in devices such as imaging equipment for miniature sized cameras, which help doctors in their patient diagnosis, without impacting the picture quality. HDI PCBs have become popular due to their small size, high quality and versatility.
8. LED Printed Circuit Boards
LED PCBs are specific types of printed circuit board, designed for use in a wide array of lighting modules and applications. A number of light emitting diodes (LEDs) are mounted to a PCB forming a completed circuit, allowing full control of their behavior through various types of chips or switches.

What are they used for?
Countless industries and applications rely on LED PCBs to control lighting arrays in multiple devices and setups. Common examples include:
Automotive lighting
Street and tunnel lighting
Indicators and display panels used in telecoms devices and computing
Torches, flashlights and work lamps
Signal lighting
Medical room and device lighting
LED PCBs have a number of distinct qualities and characteristics that make them especially well suited to these kinds of uses. Among the most important are:
Economy – LED components are fairly cheap to buy, and very efficient to run
Reliability and longevity
Low power draw
Low profile, lightweight
Fairly resistant to the effects of dirt and moisture ingress
Versatile – highly programmable, and sold in a diverse array of colors/sizes

Prototyping & Production
The diverse range of companies that we have made blank PCB boards for have benefitted from NOA Labs offering one of the fastest lead-times, with most batches being fabricated within 5 working days as standard. And many customers have saved valuable time with their product development by taking advantage of our same day prototyping service.
Your blank PCBs can be produced within 8 hours from receipt of your Gerber files, speeding up your PCB manufacturing services. Our dedicated team of highly qualified professional technicians are experts in delivering to tight deadlines and demanding specifications, often working under strict NDA protocols for a variety of major global brands. Our pricing is highly competitive, our turnaround times are remarkably quick, and we’re always proud to be able to guarantee your satisfaction with the results.